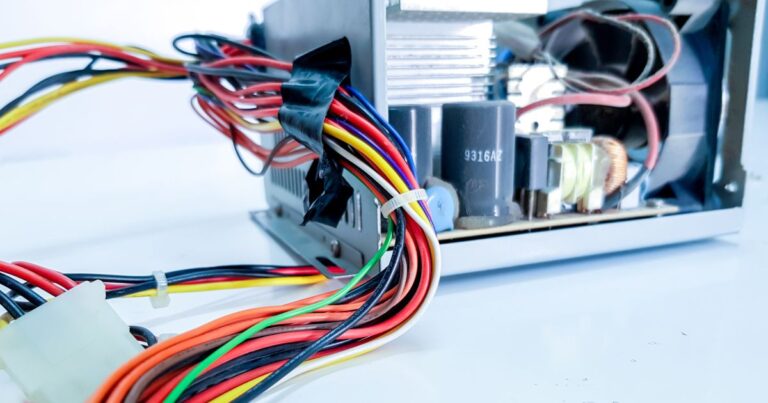
PCBA, or Printed Circuit Board Assembly, and cable assemblies form the backbone of modern electronic products. Nearly every electronic system relies on these two elements working in precise coordination to manage power, data, and control signals.
Speed to market remains a driving force across industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, and consumer electronics. Product teams face constant pressure to shorten development cycles while maintaining strict quality and reliability targets.
Bundling cable assembly with PCBA production offers a proven method to accelerate delivery schedules, reduce production friction, and simplify logistics.
Coordinated manufacturing allows both assemblies to progress together instead of moving through disconnected vendor pipelines. Integrated production also removes common communication gaps that slow projects and introduce errors.
Scenarios Where Bundling Makes Sense

Bundled manufacturing delivers the greatest impact under specific project conditions.
Timeline pressure, design dependency, and regulatory demands often push teams toward integrated production strategies.
Application Specific Requirements
Harsh operating environments demand close coordination between boards and cables.
Systems like automotive PCB assemblies, aerospace, and medical devices impose strict expectations around durability, insulation, and sealing.
Automotive, aerospace, and medical systems impose strict expectations around durability, insulation, and sealing.
Several environmental and regulatory factors often drive bundling decisions:
- High temperature operation requiring PTFE or silicone cables rated above 150 degrees Celsius
- Quality frameworks such as ISO 13485, AS9100, IPC A 610, and IPC 620
- EMI heavy environments requiring controlled shielding strategies
- Vibration prone devices needing reinforced strain relief and mechanical support
Integrated production helps confirm that both assemblies meet these demands consistently.
Tight Project Timelines
Compressed schedules benefit strongly from bundled production. Vendor handoffs disappear, and production cycles shorten due to shared planning and synchronized execution.
Clear documentation and early component definition speed layout and assembly work. Rapid prototyping services and flexible production lines support urgent timelines, especially during early validation or pilot builds.
Design Interdependency
Board stack up, trace impedance, and connector positioning often depend directly on cable characteristics. High speed or high frequency systems demand shielded cables and matched impedance routing to preserve signal integrity at data rates reaching 20 Gbps.
Industrial designs frequently require boards to support strain relief features or thermal dissipation structures that interact directly with cable assemblies. Separate sourcing complicates these dependencies.
High Mix Low Volume Production
Programs involving multiple configurations or evolving specifications benefit from unified manufacturing. Frequent changes remain easier to manage when both assemblies share a single production workflow.
Small batch runs without minimum order requirements support prototyping, niche devices, and early market testing while maintaining compliance with established cable and board assembly standards.
The Role of PCBAs and Cable Assemblies
Electronic systems rely on a close relationship between circuit boards and interconnect solutions. Performance, reliability, and manufacturability depend on how well these elements function individually and how effectively they operate together inside a finished product.
PCBA Functions
Printed circuit boards operate as a central control hub, routing and regulating electrical signals among:
- Processors
- Sensors
- Memory modules
- Power components
Signal timing, voltage stability, and reliability depend heavily on layout precision and assembly quality.
Manufacturing methods typically rely on surface mount technology or through hole assembly. Selection depends on factors such as mechanical stress, vibration exposure, current load, and long term durability.
Automotive and aerospace systems often require stronger mechanical anchoring, while compact consumer electronics favor dense surface mount layouts.
Cable Assembly Functions
Cable assemblies act as interconnect systems that link internal boards or connect devices to external interfaces such as displays, USB ports, HDMI connectors, or power supplies. Data integrity and power stability rely on correct cable selection and termination quality.
Functionally, cable assemblies serve as a nervous system that carries signals and power across a device. Shielding, insulation, strain relief, and electromagnetic interference protection play critical roles depending on application demands. Poor cable design can degrade signal quality or shorten product lifespan.
Importance of Integration
Signal quality, mechanical tolerances, and thermal behavior depend on coordinated design between boards and cables.
Connector placement, impedance control, and environmental resistance perform more predictably when planned together instead of handled in isolation.
Integrated design allows tighter alignment between cable geometry and PCB routing. Impedance targets remain consistent across connectors and traces, while mechanical features such as mounting points and strain relief receive proper clearance and support.
Environmental durability improves when vibration, heat, and moisture exposure are evaluated across both assemblies as a unified system rather than as separate parts.
Summary
Bundling PCBA and cable assembly aligns well with fast tracked programs, high reliability products, and customized or high mix production runs.
Coordinated manufacturing improves delivery speed, cost efficiency, and product quality when supported by experienced production partners.
Integrated design and synchronized execution remove friction that slows development and introduces risk.

